July 25th 2024
Embracing the future of TMS therapy for success

Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) therapy has rapidly transformed the landscape of mental health treatment, offering hope and relief to individuals battling conditions like depression, anxiety, and beyond. As we stand at the precipice of a new era in neuroscience and psychiatric care, it’s essential to explore the promising horizons that lie ahead for the future of TMS therapy.
Imagine a future where TMS therapy is not just a treatment option but a cornerstone of personalized mental health care. In this future, doctors with private clinics can expect to witness a paradigm shift in how we approach and deliver psychiatric interventions. Here’s a glimpse into what the future may hold for TMS therapy:
Precision Medicine
One of the most exciting prospects for TMS therapy is the advent of precision medicine. Just as advancements in genetics have paved the way for personalized cancer treatments, TMS therapy holds the potential for tailored interventions based on an individual’s unique brain circuitry and biomarkers. Doctors in private clinics can anticipate leveraging cutting-edge technologies like functional neuroimaging and machine learning algorithms to optimize treatment protocols and enhance therapeutic outcomes [1].
Expanded Indications
While TMS therapy has primarily been associated with the treatment of depression, the future holds promise for its expanded use across a broader spectrum of mental health disorders. From anxiety and OCD to PTSD and addiction, TMS therapy is emerging as a versatile tool in the psychiatrist’s arsenal, offering targeted relief for diverse patient populations. With ongoing research and clinical trials exploring new indications, doctors can expect TMS therapy to play an increasingly integral role in multidisciplinary treatment approaches [2].
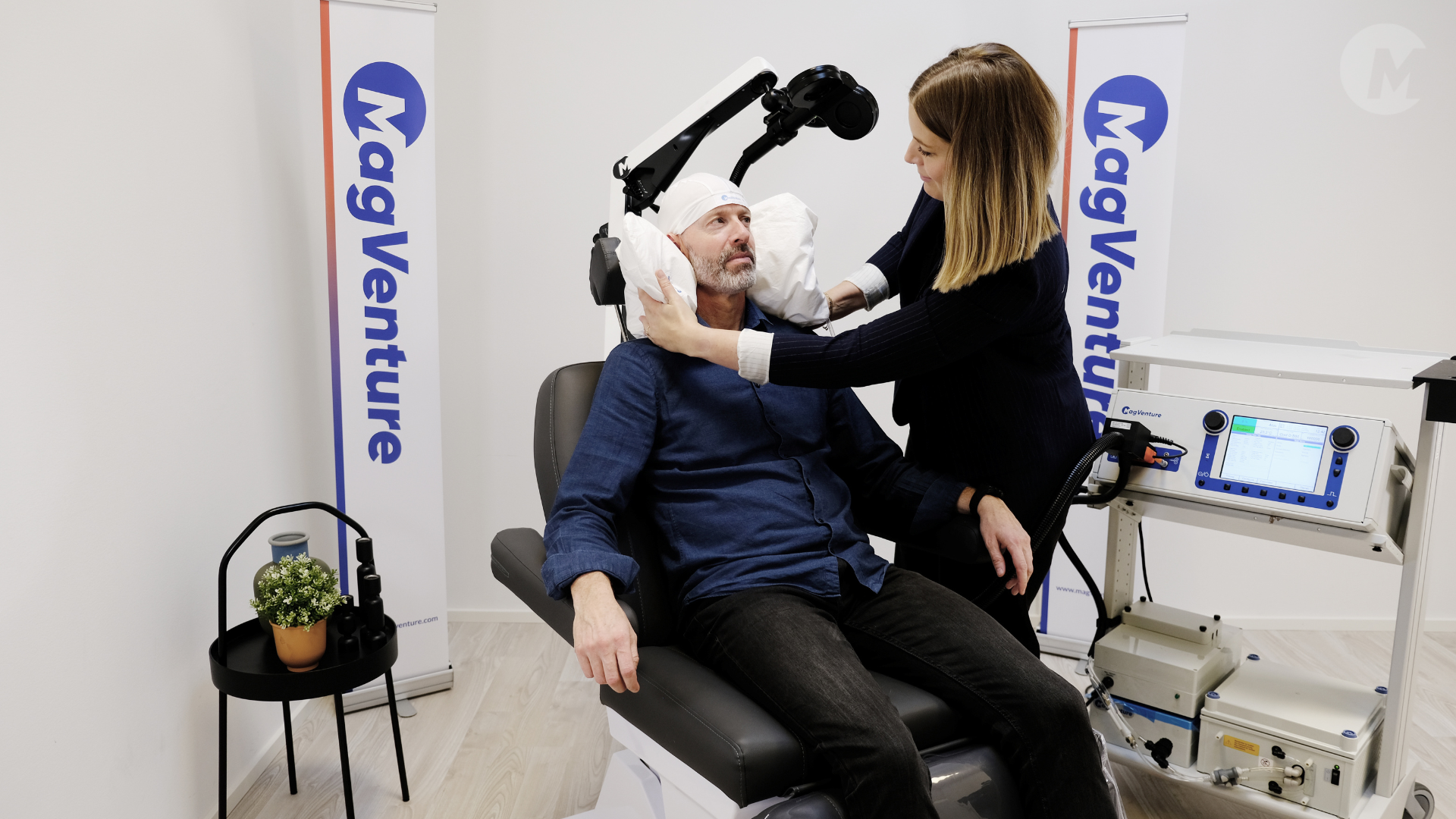
Technological Innovations
As technology continues to evolve at a rapid pace, so too will the tools and techniques used in TMS therapy. From advancements in coil design and stimulation parameters to the integration of real-time neurofeedback systems, doctors can anticipate a wave of technological innovations that will enhance the precision, efficacy, and patient experience of TMS therapy. Moreover, the development of portable TMS devices could democratize access to treatment, allowing patients to receive therapy in the comfort of their homes under remote supervision [3].
Combination Therapies
The future of TMS therapy may not be limited to standalone interventions but rather integrated into comprehensive treatment regimens. Doctors in private clinics can explore the synergistic effects of combining TMS therapy with other modalities such as psychotherapy, pharmacotherapy, and lifestyle interventions. By tailoring treatment plans to address the multifaceted nature of mental illness, clinicians can optimize outcomes and promote long-term recovery for their patients [4].
Neuroplasticity and Beyond
At the heart of TMS therapy lies the concept of neuroplasticity—the brain’s remarkable ability to reorganize and adapt in response to external stimuli. Looking ahead, doctors can expect to uncover new frontiers in our understanding of neuroplasticity and its implications for mental health and well-being. By harnessing the innate plasticity of the brain, TMS therapy may hold the key to unlocking novel avenues for neurorehabilitation, cognitive enhancement, and resilience-building [5].

In conclusion, the future of TMS therapy is brimming with potential, offering hope for individuals grappling with mental health challenges. As doctors navigate this ever-evolving landscape, they can draw inspiration from the pioneers and innovators shaping the field of neuromodulation. By embracing the future of TMS therapy with curiosity, creativity, and compassion, we can chart a course towards a brighter tomorrow—one where healing and transformation are within reach for all.
References
- Lefaucheur, Jean-Pascal, et al. “Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS).” Clinical Neurophysiology 125.11 (2014): 2150-2206.
- Rossi, Simone, et al. “Safety, ethical considerations, and application guidelines for the use of transcranial magnetic stimulation in clinical practice and research.” Clinical Neurophysiology 120.12 (2009): 2008-2039.
- Philip, Noah S., and Mark S. George. “Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for the Treatment of Mood Disorders: A Review.” The Journal of ECT 34.3 (2018): 183-193.
- George, Mark S., and Robert H. Belmaker. “Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Neuropsychiatry.” American Psychiatric Publishing, 2000.
- Lefaucheur, Jean-Pascal, et al. “Neurological adverse events associated with repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS).” Clinical Neurophysiology 126.9 (2015): 1719-1725.









